HEART
The Heart
Location:
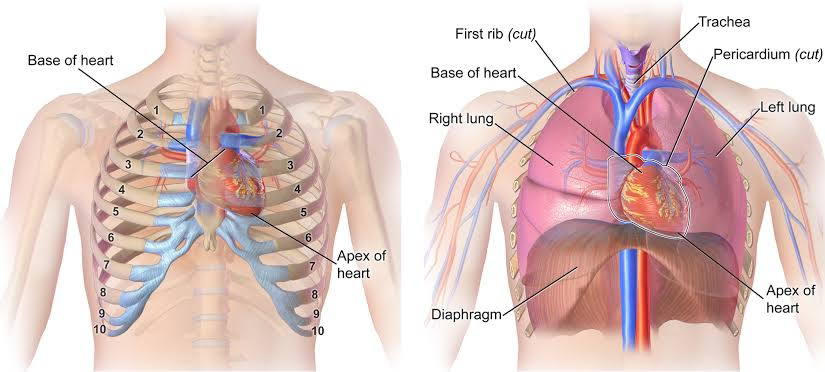
- The heart is located in the thoracic cavity
- Posterior to the sternum
- Superior to the diaphragm
- Between the lungs
- The tip of the heart is called the 'apex'
The heart has:
3 layers
- Pericardium
- Endocardium
- Myocardium
4 chambers
- 2 atrium
- 2 ventricles
4 valves
- Mitral
- Aortic
- Tricuspid
- Pulmonary
Function
- The heart pumps oxygen and nutrient rich blood to the organs, tissues and cells of the body, and eliminates waste products
- Blood is carried from the heart to the organs through arteries, arterioles and capillaries
- Blood returns to the heart through venules and veins
Layers of the Heart
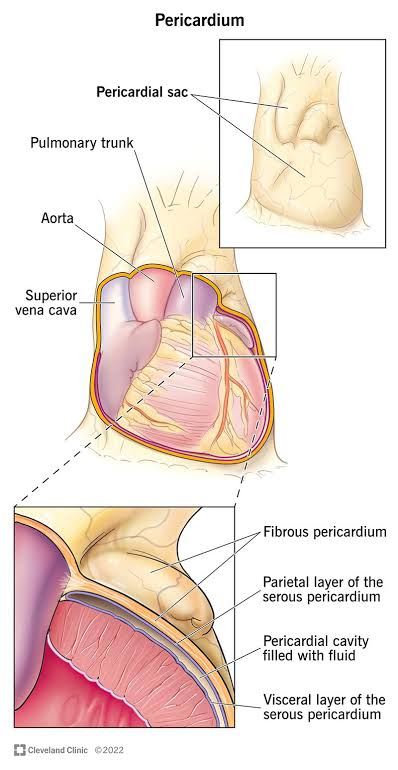
Pericardium:
The heart is surrounded by a fibro serous sac called pericardium
The function of the pericardium is :
- To limit cardiac distension and restrict excessive movement
- To protect and lubricate
The pericardium is composed of :
- Innermost/deepest layer of the heart
- Lines the heart chambers and the valves
- Smooth thin lining to reduce friction of blood flow through the chambers
- Cardiac conduction system located in this layer
Myocardium:
- Middle, thickest layer of the heart
- Contains the muscle fibers which are responsible for pumping
- Contraction of this layer allows blood to be pumped through to the blood vessels
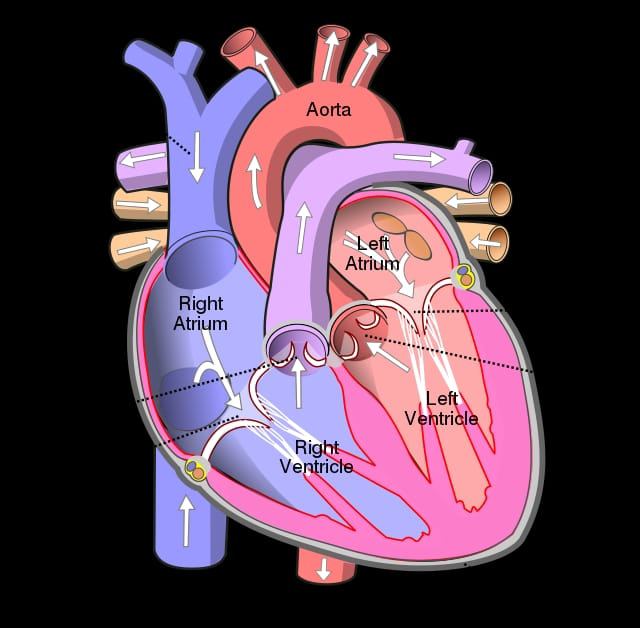
Chambers of the heart
He heart is divided into four chambers:
Right Atrium, Right Ventricle
Left Atrium, Left Ventricle
The upper chambers are:
The atria (Right, Left)
The right atrium:
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the:
- Superior vena cava (head and upper body)
- Inferior vena cava (legs and lower torso)
The left atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the:
- Pulmonary vein
Lower chambers
The lower chambers are :
The ventricles (Right, Left)
The right ventricles:
Receives deoxygenated blood as the right atrium contracts
The left ventricles
Receives oxygenated blood as the left atrium contracts
Valves of the heart
The valves are located within the chambers of the heart.
The function of the valves:
Controls the direction of blood flow, allows one way flow of blood
1.throught chambers
2.from the heart to the body
The four valves are known as :
- The tricuspid valve
- The pulmonic Or pulmonary valve
- The mitral valve
- The aortic valve
The tricuspid valve:
- Is an atrioventricular valve, situated between the atria and the ventricle
- Controls the opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle
The mitral valve:
- Is an atrioventricular valve, situated between the atrial and the ventricle
- Controls the blood between the left atrium and the left ventricle
The pulmonic or pulmonary valve:
- Is a semi lunar valve which controls the blood leaving the heart
- Situated between the right ventricle and the pulmonary valve
- Controls the flow of blood from the right ventricle
- Prevents blood flow back to the right ventricle, as it relaxes
The aortic valve:
- Is a semi lunar valve which controls the blood leaving the heart
- Controls blood flow between the left atrium and the aorta
Pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary circulation is :
The carriage of oxygen depleted blood away from the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary artery . The return of oxygen rich blood to the heart via the pulmonary vein.
Pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary circulation and the heart
- The inferior and superior vena cava carry oxygen depleted blood to the relaxed right atrium of the heart
- The right atrium contracts and blood travels through the tricuspid valve into tha relaxed right ventricle
- The right ventricle contracts, the blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery to the lungs
- As exchange occurs in the lungs
- O2 is released and oxygen is absorbed
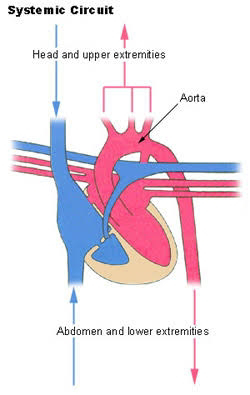
Systemic circulation is:
The carriage of oxygen rich blood away from the heart to the body. The return of oxygen depleted blood back to the heart
Systemic circulation and the heart
- Oxygen rich blood travels from the lungs via the pulmonary veins to the left atrium
- The left atrium contracts, and blood flows through the mitral valve into the relaxed left ventricle
- The strong left ventricle contracts and pumps oxygen rich blood through the aortic valve into the aorta
- The aorta carries blood to the organs of the body
The conducting system
Cardiac conduction is :
The rate the heart conducts electrical impulses. The electrical pulses determine the order in which the chambers contract the heart rate.
The Sinoatrial node (SA)
- It also known as the pace maker of the heart
- Located in the upper wall of the right atrium
- Made up of nodal tissue both muscle and nervous tissue
- Here the electrical impulses begins
The atrioventricular (AV) node
- Its located between the atria and ventricles of the heart
- Made up of nodal tissue
- The electrical impulses is carried from the SA node, and the AV node is stimulated.
The AV bundles start to divide further into :
-Purkinje fibres
Purkinje fibres:
- Located at the end of the AV bundle branches, at the base of the heart
- The purkinje fibres are responsible for the contraction of the ventricles.
A summary
- The heart is located in the thoracic cavity
- The heart has 3layers , 4 layers, 4valves
- The heart pumps oxygen and nutrient rich blood to the organs, tissues and cells of the body, and eliminates waste products
- The cardiovascular system: pulmonary circulation, systemic circulation, coronary circulation
- Cardiac conduction is : the rate heat conducts electrical impulses
- The path the impulses travel: sinoatrial node (SA node), Atrioventricular node (AV node), bundle branches, purkinge fibres: the heart rate
Dr. Mahalakshmi Raghunath









Comments
Post a Comment